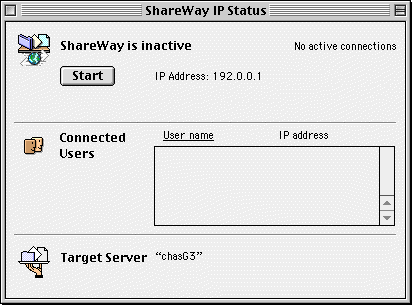
Figure 1. Status Window
ShareWay IP includes two versions of the software; a faceless background-only version and a traditional foreground version (see Background & Foreground Versions). On Mac OS 9, the ShareWay installer installs the background version as the "active" version (upgrading the background version included with the OS), while on pre-OS 9 systems, you choose which version to use.
All configuration of ShareWay IP is done through the foreground version. How you actually administer changes to ShareWay IP depends on your Mac OS version number and which version (foreground or background) of ShareWay you are using to implement File Sharing over IP:
Changes to ShareWay include:
The status window of ShareWay IP's foreground version is shown below in Figure 1.

Figure 1. Status Window
ShareWay IP's status window displays important information:
This window will display a 'not available' warning next to the server name if ShareWay IP has not been able to contact the ShareWay machine's personal file sharing. ShareWay IP periodically checks the availability of file sharing, updating the 'not available' display as appropriate. ShareWay might display 'not available' if:
This window may also show that the IP address is not available. This would happen if:
ShareWay IP uses a serial number mechanism to easily convert evaluation versions of the software to paid-for versions and to prevent unauthorized duplication of the software. It is available as an evaluation version that will stop working 10 days after the date it is first run. Until expiration, the eval version has all the functionality of a full working version. An eval version of ShareWay can be converted to a permanent working version by giving it a valid serial number.
Background version - Serial numbers for the background version are entered through the foreground version. For details, see ShareWay IP Administration.
Foreground version - When an unexpired eval of the ShareWay IP foreground version is launched, a dialog appears with the options "Enter Serial Number..." and "OK". Clicking OK lets you run the software as an eval. Clicking "Enter Serial Number..." brings up a dialog which allows you to enter a serial number and convert the software into a permanent working version. Enter the serial number you were provided when you paid for the product, and click OK.
When an expired eval version is launched, a dialog appears with the options "Enter Serial Number..." and "Quit". To convert an expired version into a full working version, click "Enter Serial Number...", enter a serial number and click OK.
The "Enter Serial Number..." dialog can also be brought up while the product is running. Stop ShareWay IP, choose "Enter Serial Number..." from the File menu, and proceed as described above.
If more than one copy of ShareWay IP is used, each copy must have a unique serial number. A ShareWay serial number is registered on the network (and checked for duplicates) when ShareWay is started, not when the serial number is first entered.
Serial numbers for previous versions of ShareWay IP will not work with ShareWay IP 3.0. You must purchase an upgrade to ShareWay IP 3.0 to obtain a valid 3.0 serial number. To purchase a serial number for an eval copy, or to obtain a lost serial number, contact Open Door Networks.
ShareWay IP has the option of logging significant events relating to ShareWay IP, such as:
To turn ShareWay's logging feature on (or off), choose "Turn Logging On" (or "Turn Logging Off") from the File menu.
When logging is enabled, a file called "ShareWay IP Log" is written to the ShareWay Macintosh's Preferences folder. ShareWay IP always appends to an existing log file. ShareWay IP's log file can be analyzed in real-time by Open Door's LogDoor Real-time Server Monitor. LogDoor provides an up-to-the-minute view of accesses to your server, which may be important for both security and management reasons. See ShareWay IP Log File for details of the log file format.
Changing ShareWay's TCP Port Number
Under certain circumstances it may be desirable to change ShareWay IP's TCP port number from its default of 548. For example, if an installation has a firewall which blocks port 548, it may be easier, for administrative reasons, to change ShareWay's port number than to change the firewall. It is also possible that another application on the ShareWay machine might use port 548.
Note that changing ShareWay's TCP port number requires clients to specify the new port number when accessing the ShareWay machine, if they are entering the URL directly. Suppose, for example, that ShareWay IP on a given machine had an AFP URL of afp://192.0.0.1/; if ShareWay was changed to use TCP port 8548, its AFP URL would become afp://192.0.0.1:8548/. If ShareWay's Service Location Protocol feature is utilized, the correct port number will be determined automatically, and need not be entered by the client.
To bring up ShareWay's TCP Port dialog, stop ShareWay if it is not already stopped and select "Set Port Number..." from the File menu. The dialog appears as shown below in Figure 2.

Figure 2. Port Number Dialog
ShareWay's port number is initially set to 548, the default for AFP. To change ShareWay's port number to another value, just enter the value (between 1 and 65535) and click OK. To prevent port number conflicts, it is recommended that alternate port numbers be 8548 or above. To revert to ShareWay's default value, click "Revert to Default" and then click OK.
Number of Users Supported
Because Mac OS personal file sharing only supports a maximum of 10 simultaneous users, ShareWay IP Personal Edition also supports only 10 simultaneous users.
With OS 8.5 and later, online help for ShareWay IP is available. When installed, help is accessible in two ways:
Either method will invoke ShareWay's online help, which is structured much like this user guide. Note that when running the background-only version of ShareWay, online help is only available through the Finder's Help menu's Help Center, since the background application has no menus.
Background & Foreground Versions
ShareWay IP Personal includes two versions of the ShareWay application; a background-only version called "ShareWay IP Personal Background", and a foreground version called "ShareWay IP Personal". On Mac OS 9, the ShareWay installer puts the background version in the Extensions folder, where it takes the place of OS 9's built-in File Sharing over IP. The installer also puts the foreground version in a ShareWay folder on your hard drive, to be used to configure the background version. On pre-OS 9, the installer puts both versions in a ShareWay folder on your hard drive. The advantages and disadvantages of each version are summarized below in Table 1.
| ShareWay IP Personal | ShareWay IP Personal Background |
| Displays users connected to ShareWay, and their IP addresses | No user interface. ShareWay does not show up in the application menu or "About this Computer" window. The File Sharing Control Panel's Activity Monitor displays all users connected to file sharing, although it does not distinguish AppleTalk connections from IP. |
| Users can accidentally quit ShareWay, or reconfigure ShareWay's security features. | Cannot be accidentally quit, and administration can be controlled. |
| Security and logging reconfiguration can be done without disconnecting current users. | Any reconfiguration (security, logging, port number or serial number) requires launching the foreground version, which will disconnect all current users. |
| In Mac OS 9's Multiple Users environment, all connected ShareWay clients are disconnected when a user logs off. | In Mac OS 9's Multiple Users environment, users can log off without disconnecting ShareWay clients. |
Any errors encountered in the background application will be posted as alerts, after which the background application will quit.
Installing the Foreground Version on Mac OS 9
On Mac OS 9 you may wish to install the foreground version of ShareWay IP 3.0 in the Extensions folder, in place of the background version. Doing so makes ShareWay's user interface available at all times. To install the foreground version:
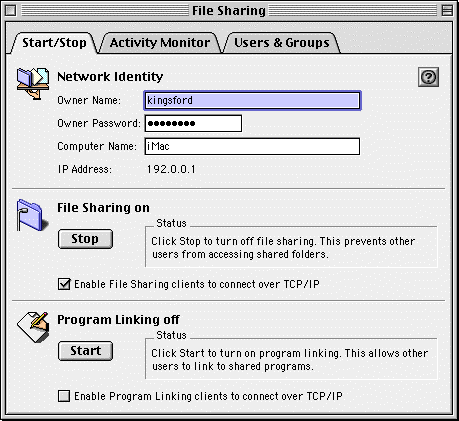
Figure 3. File Sharing Control Panel
Mac OS 9 and Multiple Users
When running ShareWay IP in Mac OS 9's Multiple Users environment, all users share the same preferences file and log file. These files are stored in the System Folder's Preferences folder.
If a user is set up as a Normal User, they will be able to change ShareWay IP's configuration, and those changes will affect all other users. It is therefore recommended that all users be set up as Limited Users, and denied access to the foreground version of ShareWay IP. In this way, only the Owner will be able to configure ShareWay IP.
In the Multiple Users environment, it is recommended that you use the background version of ShareWay IP. The foreground version will quit whenever a user logs off the ShareWay machine, causing all of ShareWay's connected clients to be disconnected. The background version will keep running when a user logs off, providing continuity for ShareWay's connected clients.
![]() Back to Table of Contents
Back to Table of Contents
![]() Back to Getting Started (Pre-OS 9)
Back to Getting Started (Pre-OS 9)
![]() Forward to Security
Forward to Security